Network attack monitoring with PRTG
Maintain the security of your network with the help of monitoring
- Monitor firewalls, virus scanners, security software, backups, and more
- Identify and eliminate weak spots in your IT infrastructure
- Analyze historical data for anomalies and unusual activities
PRTG network attack monitoring: What you’ll find on this page
- The threat of network attacks is growing
- What does network monitoring have to do with network attacks?
- What computer network attack monitoring looks like in PRTG
- 5 reasons why to choose PRTG as your network attack monitoring tool
- 3 ways to use PRTG to fight and prevent network attacks
- Monitor network attacks: FAQ
PRTG makes network security attack monitoring as easy as it gets
Custom alerts and data visualization let you quickly identify and prevent cyber security and data breach issues.
The threat of network attacks is growing
Companies have never been as vulnerable to network attacks as they are today. Hackers operate globally and generate income across the Internet.
Companies have come to realize that as their virtual presence grows, so does the number of gateways in their networks. These interfaces are used by hackers in an increasingly sophisticated manner, creating a problem that only gets worse as a company’s IT infrastructure becomes more complex.
Network attacks can damage your company in serious ways:
- Compromised websites and social media accounts
- Damaged brands and loss of trust due to leaked customer information or credit card data
- "Ransom" payments to regain access to your systems
- Theft of business secrets which incurs a cost of developing new security strategies
- Sales losses due to disrupted company activities following DDoS attacks, flooding, or botnets which diminish computing capacity
- Extensive property damage, injuries, or even deaths due to the hacking of critical infrastructures
- Personal liability including the incarceration of management if legal requirements have not been adhered to
What does network monitoring have to do with network attacks?
Network monitoring: A fundamental tool for IT security
Comprehensive network monitoring tools such as Paessler PRTG are vital for maintaining the security of your network – for what good does a firewall do that’s not available, or backup software that malfunctions?
With network monitoring software, you can keep a constant eye on security components, antivirus software, and backups, and automatically be warned in the event of trouble.
Network traffic recording: Detect suspicious activity
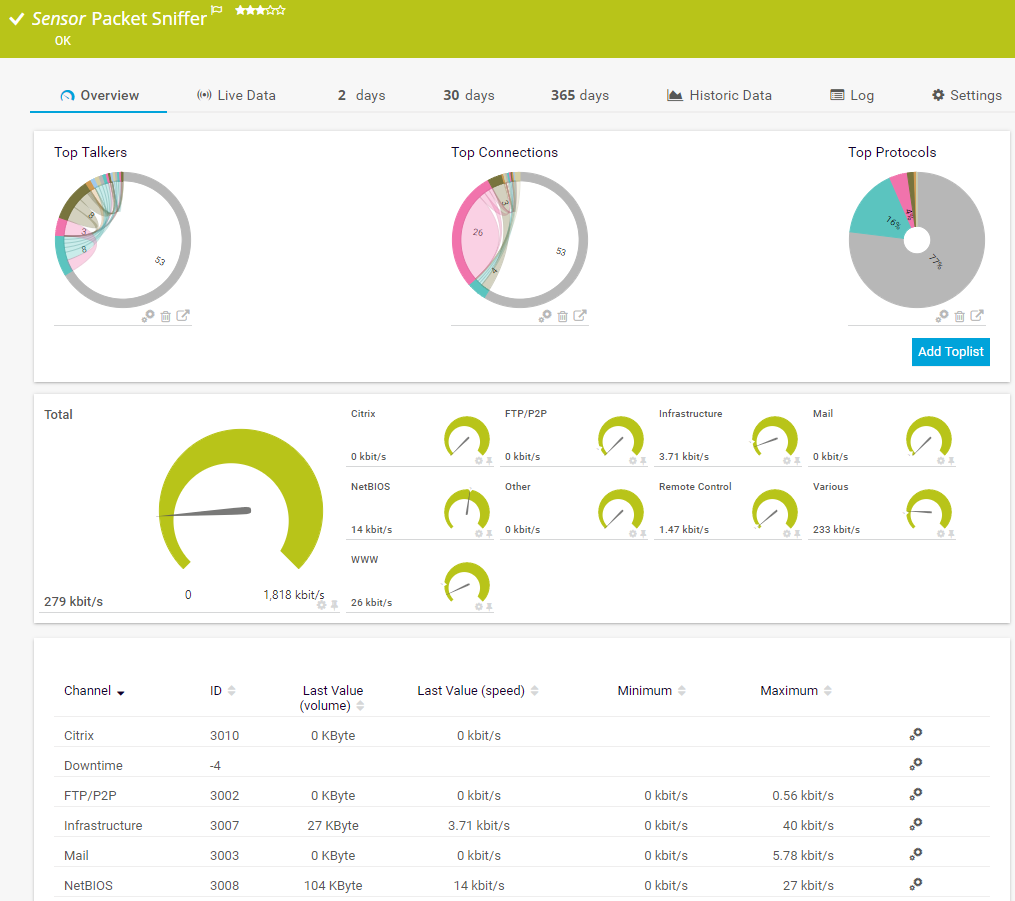
Network traffic analysis, which is included in PRTG, lets you monitor and check data traffic for suspicious behavior such as unusually high traffic loads.
It also helps you determine which data and systems are affected by network attacks that already happened. By evaluating historical data records, you can not only prevent cybersecurity issues like DDoS attacks, but also significantly reduce downtime.
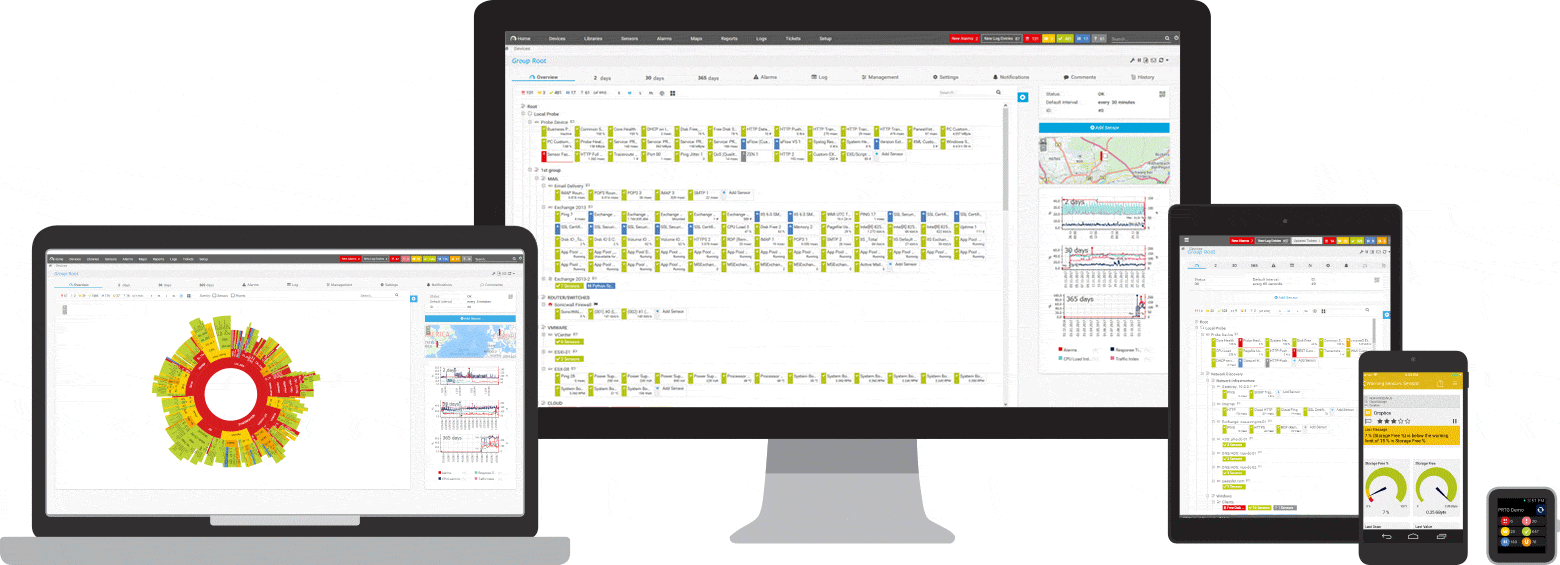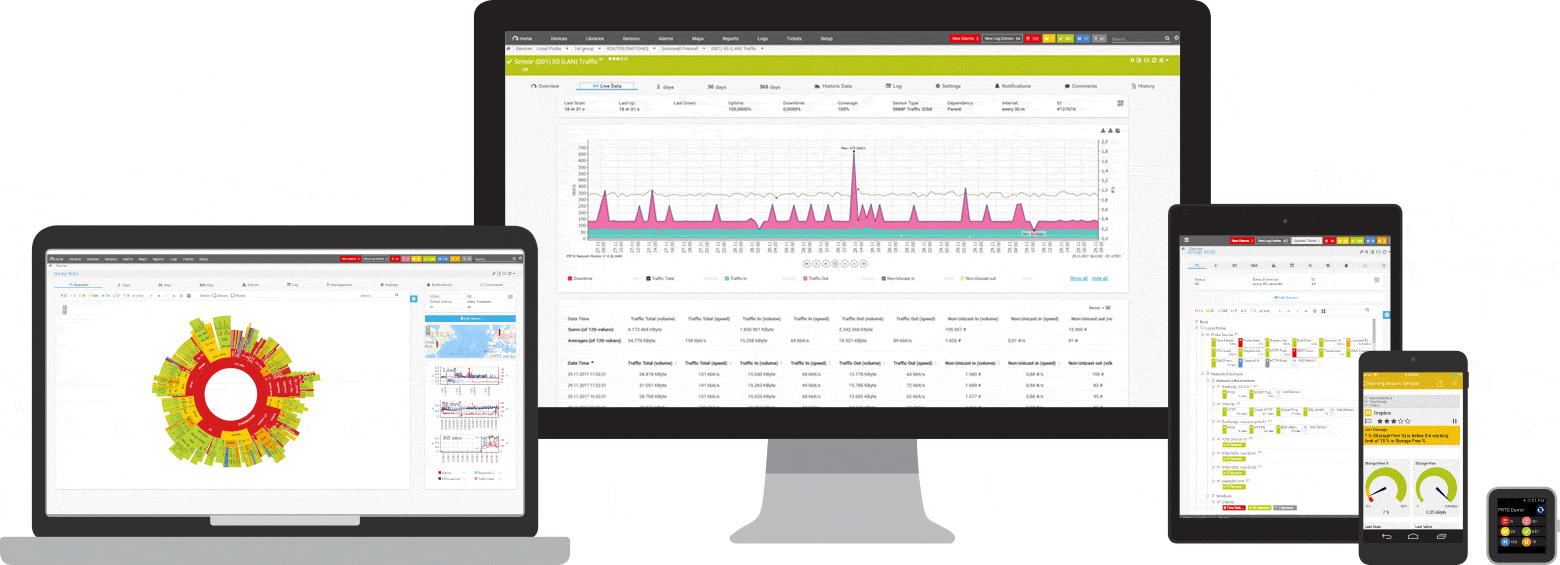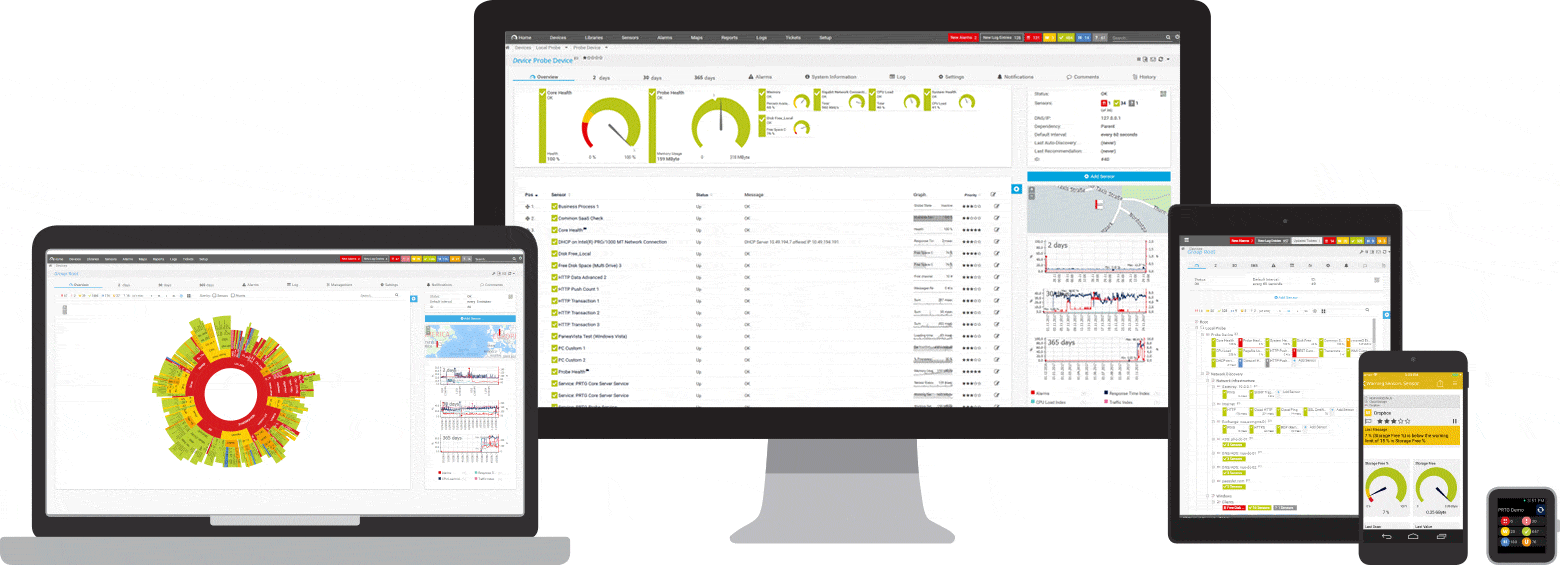
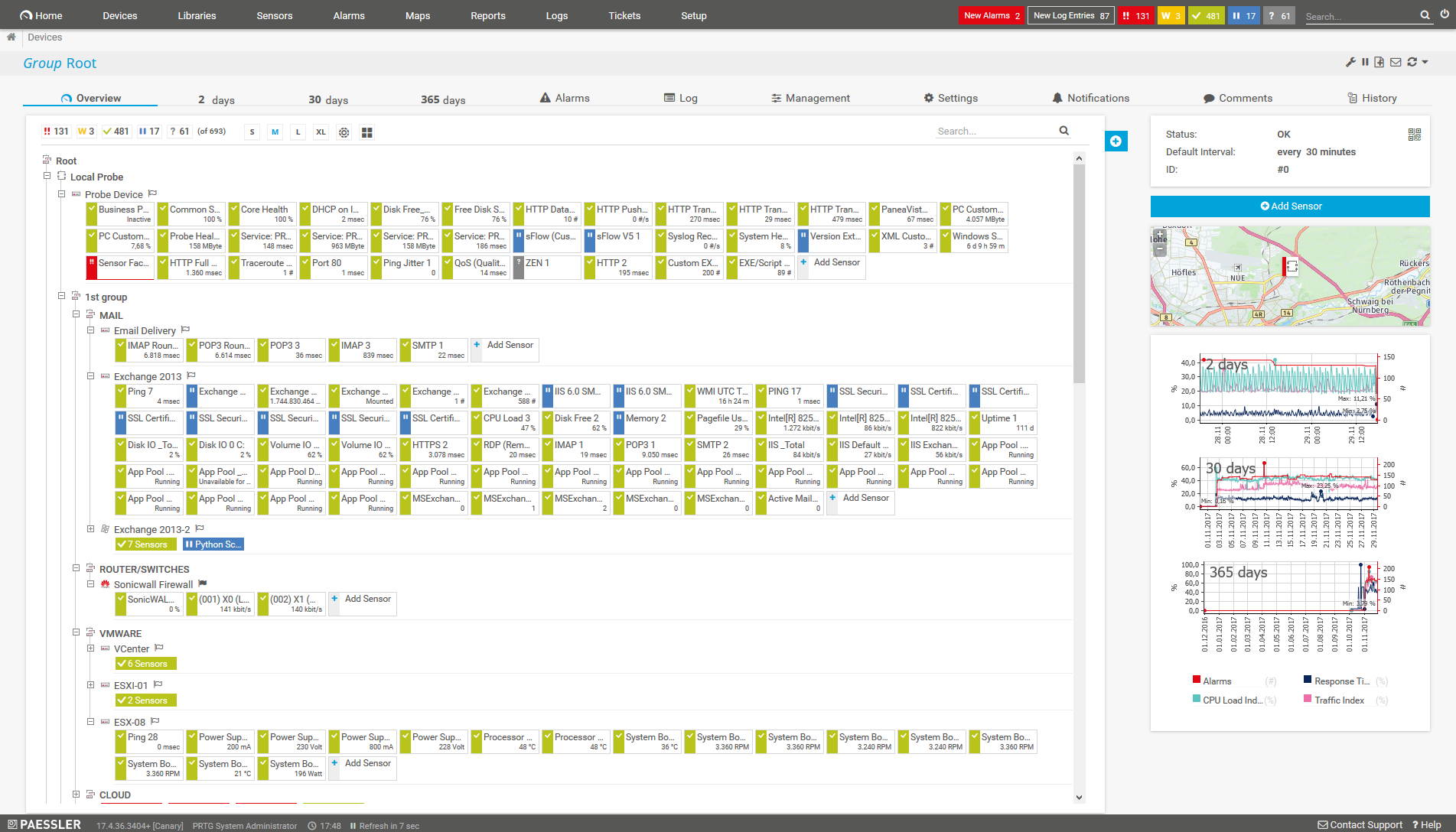
What computer network attack monitoring looks like in PRTG
Diagnose network issues by continuously tracking the security of your entire network. Show unauthorized access, unusual network traffic, data breaches, unavailable firewalls, or malfunctioning antivirus software in real time. Visualize monitoring data in clear graphs and dashboards to identify problems more easily. Gain the overview you need to troubleshoot weak spots in your IT infrastructure that can present a security threat.
Start monitoring network attacks with PRTG and see how it can make your network more reliable and your job easier.
5 reasons why to choose PRTG as your network attack monitoring tool
Reduce risks & complexity with centralized monitoring
For monitoring your network, PRTG is more effective at reducing risks and complexity than several individual tools working together.
Our all-in-one software effectively monitors all the devices and parameters in your entire network: servers, storage, connected devices such as routers, computers, and switches, traffic, and more. This helps to eliminate risks arising from weak spots and compatibility problems between tools.
Early warning system for suspicious network activity
PRTG acts as an early warning system against suspicious activity and anomalies in your network traffic, which are recorded and traced. This way, you can prevent malware and hackers who have already infiltrated the network from causing additional damage.
Easy-to-read dashboards provide an overview of your monitoring data. You can also have interrelated data displayed on your dashboard to establish correlations and draw conclusions.
Identify affected computers and network bottlenecks
PRTG measures and analyzes your network traffic and lets you filter it by IP address or protocol, for example. This way, you can quickly identify potential network bottlenecks, spot unusual spikes in activity, and shut down affected applications and systems.
Also, recorded network traffic data makes it easier to identify devices affected by an attack, and to recover these computers via countermeasures or the restoring of a backup or image.
Monitor & protect security measures in your network
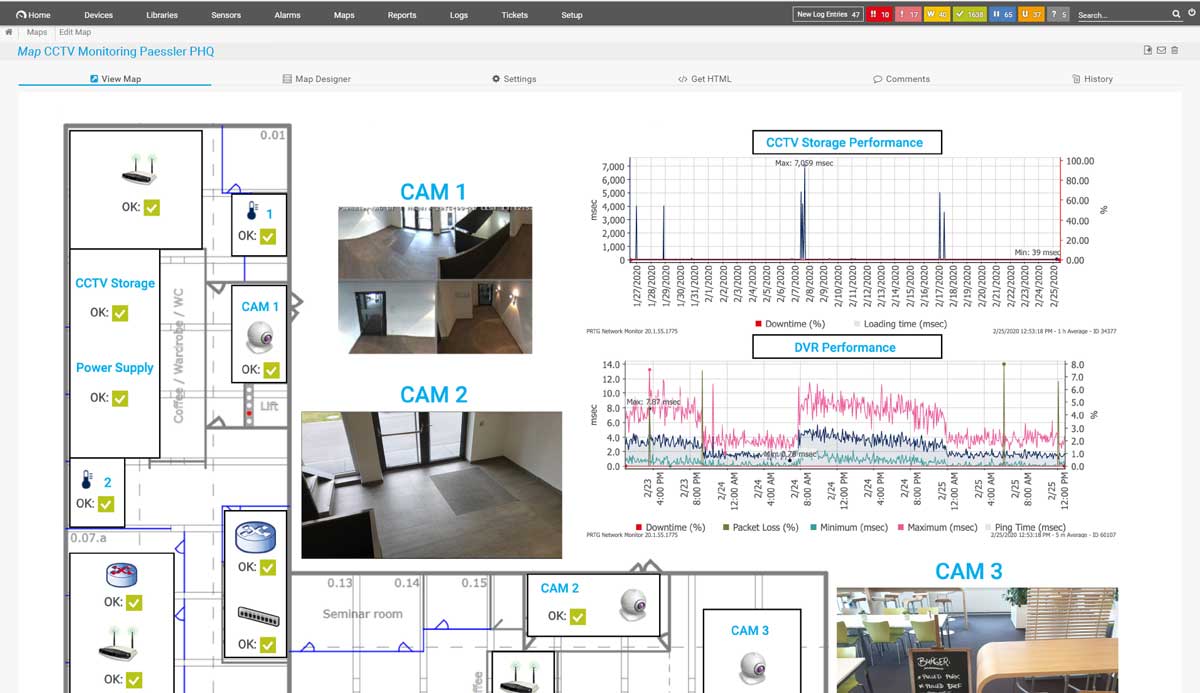
By continuously keeping an eye on firewalls, antivirus software, and other security devices and tools, PRTG can warn you in the event of downtime that may be posing a security risk to your network. Faulty backups are also recorded. You can therefore take action before things go awry.
It also checks the functionality of security-relevant hardware components such as door locks or CCTV security cameras, as well as access rights to spaces like server rooms.
Get customizable real-time notifications and alerts
PRTG comes with a highly customizable alerting and notifications system out of the box. It lets you define granular warning and error thresholds and set up different notification triggers for various escalation levels. This way, you are able to intervene before further damage occurs.
What’s more: you can choose from several notification methods such as email, SMS, push notification, and others, and even define automation scripts to shut down affected systems.
3 ways to use PRTG to fight and prevent network attacks
Set up network security monitoring
- Traffic monitoring
- Firewall monitoring
- Virus scanner monitoring
- Backup monitoring
- Server monitoring
- Server room monitoring
Analyze historical monitoring data
- Determine the details of an attack that happened
- Retrieve the network traffic recording history
- Search for specific attack patterns
- Shut down the affected device and/or applications
Check network traffic for anomalies
- Add preconfigured PRTG sensors for monitoring traffic (via SNMP, packet sniffing, or flow protocols)
- Set up threshold values and notification triggers for traffic parameters
- Search for unusual patterns such as inexplicable load peaks or abnormally heavy traffic
- Introduce countermeasures against cyber attacks
Find the root cause of the problem with our PRTG network attack monitoring solution
Real-time notifications mean faster troubleshooting so that you can act before more serious issues occur.
Your network attack monitor at a glance – even on the go
Set up PRTG in minutes and use it on almost any mobile device.

Create innovative solutions with Paessler’s partners
Partnering with innovative vendors, Paessler unleashes synergies to create
new and additional benefits for joined customers.
PRTG makes network security attack monitoring as easy as it gets
Custom alerts and data visualization let you quickly identify and prevent cyber security and data breach issues.
PRTG: The multi-tool for sysadmins
Adapt PRTG individually and dynamically to your needs and rely on a strong API:- HTTP API: Access monitoring data and manipulate monitoring objects via HTTP requests
- Custom sensors: Create your own PRTG sensors for customized monitoring
- Custom notifications: Create your own notifications and send action triggers to external systems
- REST Custom sensor: Monitor almost everything that provides data in XML or JSON format
More than just a monitoring tool:
Reasons our customers love PRTG



Still not convinced?
More than 500,000
sysadmins love PRTG
Paessler PRTG is used by companies of all sizes. Sysadmins love PRTG because it makes their job a whole lot easier.
Monitor your entire IT infrastructure
Bandwidth, servers, virtual environments, websites, VoIP services – PRTG keeps an eye on your entire network.
Try Paessler PRTG
for free
Everyone has different monitoring needs. That’s why we let you try PRTG for free.
Start monitoring network attacks with PRTG and see how it can make your network more reliable and your job easier.
|
PRTG |
Network Monitoring Software - Version 25.1.104.1961 (April 7th, 2025) |
|
Hosting |
Download for Windows and cloud-based version PRTG Hosted Monitor available |
Languages |
English, German, Spanish, French, Portuguese, Dutch, Russian, Japanese, and Simplified Chinese |
Pricing |
Up to 100 sensors for free (Price List) |
Unified Monitoring |
Network devices, bandwidth, servers, applications, virtual environments, remote systems, IoT, and more |
Supported Vendors & Applications |
|









Combining the broad monitoring feature set of PRTG with IP Fabric’s automated network assurance creates a new level of network visibility and reliability.